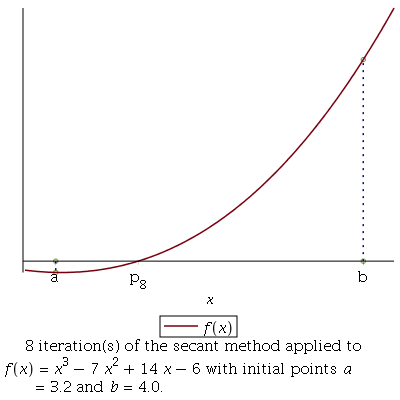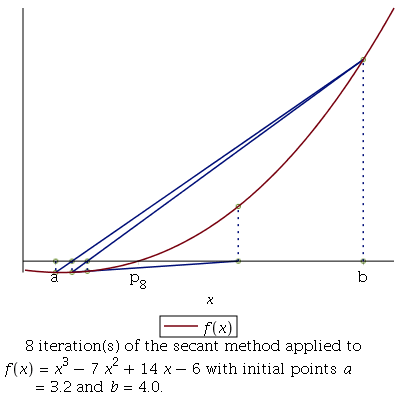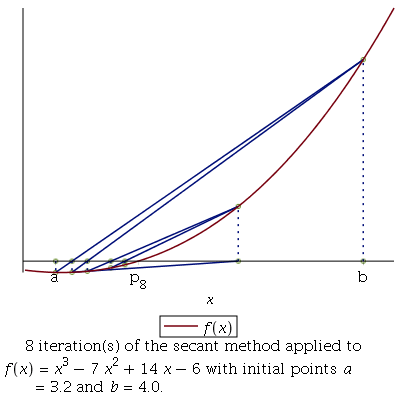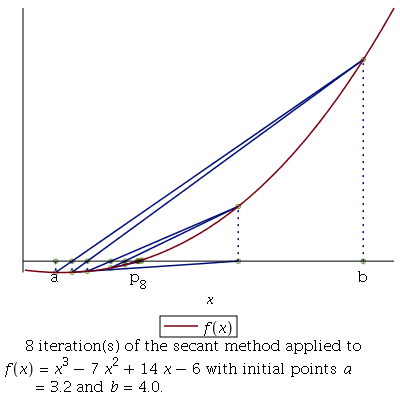
Secant Method : This method similar to the Regular-falsi method but here we don’t need to check f(a)f(b)<0 again and again after every approximation. In this method, the neighbourhoods roots are approximated by secant line or chord to the function f(x).
Algorithm :
: For any continuous function f(x),
- Find two points, say a and b such that a < b and initialize error e (depends upto what accuracy you want the result)
- Take the interval [a, b] and determine the next value of m.
m = [a*f(b)-b*f(a)] / [f(b)-f(a)]- m is the root of the given function if f(m) = 0; else follow the next step
- a=b, b=m
- Repeat step 2,3, 4 until |f(m)| < e.